A newly identified COVID-19 subvariant, NB.1.8.1, nicknamed ‘Nimbus’, is making headlines for its unusual symptom profile and rapid global spread. While health authorities including the WHO and CDC confirm that the variant does not cause more severe illness, its high transmissibility and distinctive symptoms have raised public health concerns.
🌐 What Is NB.1.8.1 (Nimbus)?
NB.1.8.1 is a recombinant Omicron subvariant first detected in China and now spreading across the UK, US, India, and Southeast Asia. It features mutations that enhance its ability to bind tightly to human cells and evade immune responses, making it more contagious than earlier strains.
⚠️ 4 Unusual Symptoms to Watch For
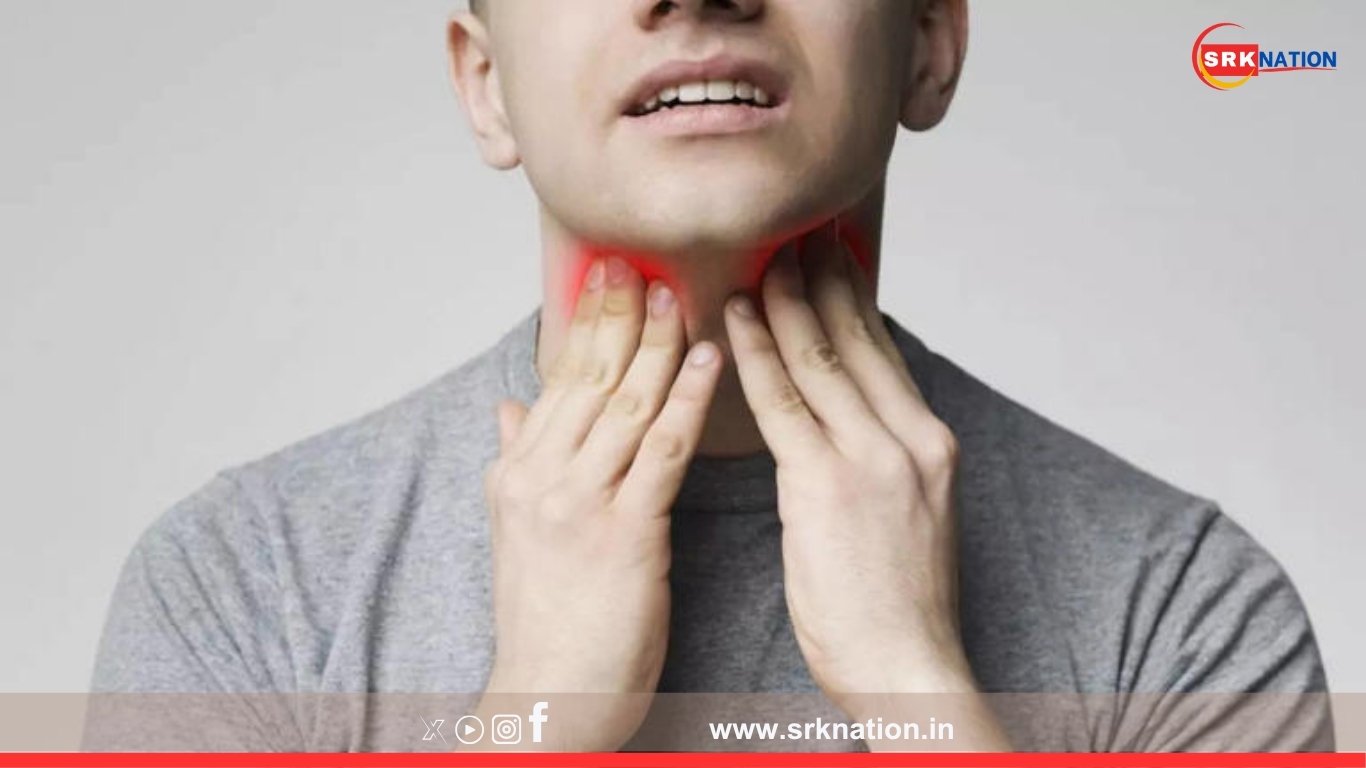
- “Razor Blade” Sore Throat
Patients describe an intensely painful sore throat, likened to “swallowing glass” or “razor blades.” This symptom appears early and is more severe than typical Omicron-related throat discomfort. - Sudden Loss of Appetite
Unlike previous variants, NB.1.8.1 often causes a sharp drop in appetite without accompanying nausea or digestive issues. Experts suggest this may be linked to inflammation affecting the brain’s appetite center. - Muscle Aches in Unusual Areas
While body aches are common in viral infections, this variant causes soreness in unexpected spots—such as the jaw, upper back, and behind the ears—raising diagnostic challenges. - Unexplained Weight Loss
Some patients report rapid weight loss due to reduced appetite and fatigue, even in the absence of gastrointestinal symptoms. This has been flagged as a potential early warning sign.
🧬 Should You Be Worried?
Despite these symptoms, NB.1.8.1 is not associated with increased hospitalization or mortality in healthy individuals. However, elderly and immunocompromised people remain at higher risk and should continue to take precautions.
Stay tuned for verified health alerts and expert guidance.